|
The more detailed information about presowing seed treatment with Albit you may find here.
Seed treatment is very important for obtaining high yield of cereal
crops. For many years, Albit has been successfully applied for seed treatment
of wheat, barley, rape, maize, legumes and other crops (Fig. 1). In this
process, Albit acts in 3 ways at the same time:
plant growth regulator, fungicide, antidote.

Fig. 1. Influence of seed treatment with Albit on
lentil germination (All-Russia Research Institute of Legumes and Groat
Crops, Oryol oblast, 2008)
Storage and sowing of pre-treated seeds. Seeds treated with Albit should be stored in an area with no light at cool room temperature (not exceeding +20°C). This area should also have adequate ventilation. We recommend to sow the seeds within one day from the treatment (with the exception of sunflower seeds). Otherwise, there is a possibility of a decline in the effectiveness of Albit: saprophytic microflora of the seeds might begin to utilize the product.
Shelf life of treated seeds can be extended up to several months in the case of joint treatment of seeds with Albit and chemical agents. Chemical agents such as fungicides or insecticides act as preservatives to Albit. Seeds treated with this tank mix can be stored for up to 2 months without any impact to Albit's effectiveness. For example, in an experiment conducted by the All-Russian Research Institute of Plant Resources (2005), seeds of sugar beet (Ramonskaya MS-73 variety) were treated with an insecticidal agent (a.i. carbofuran) together with Albit. The rate of use was 20 L/tonne, and the mix was used several times: a month and a week prior to sowing, and immediately before sowing. This treatment resulted in a 71% biological effectiveness against the root beetle. The yield averaged at 25.5–26.5 t/ha in all Albit treatment groups (21.8 t/ha in control).
Treating seeds with Albit ensures:
- Increased field germination rate
- Removed retardant effect of fungicidal treatments (antidote quality of Albit)
- Resistance of crops grown from treated seeds to the phytotoxic effect of herbicides
- Protection of plants against root diseases (including long-term protection from soil-borne rots)
- Effect of long-term immunization against leaf- and stem-targeting diseases up until the heading stage
- Forming of a potent root system and flag leaf
- Accelerated harvest (up to 14 days of advance in harvest maturity)
- Increased yield
- Decreased amount of pathogenic fungi in root area
- Accumulation of sugars (carbohydrates) in the tillering node and leaves of winter cereals. It increases frost resistance
- Antioxidant protection (for more detailed information, please, see below)
PHB and its derivatives interact with the receptors of NADPH oxidase system which are located on the surface of plant cells. Enhanced activity of NADPH oxidase in plants leads to the formation of superoxide and other reactive oxygen species (ROS) in concentrations higher than the norm but not deleterious to the plants. This process triggers expression of cascade of plant antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, peroxidases, dehydroascocorbate reductase, glutathione reductase) which are able to detoxify ROSes. Finally, the total antioxidant capacity of cells increases in 1,4–3,6 times. Increased level of antioxidant enzymes in plant cells also promotes to the higher content of ascorbate and chlorophyll (up to 100% increase to control). Since any stress (including low temperature) in plants ultimately leads to the accumulation of ROS and impairing of chlorophyll, plants pre-treated with Albit possess much higher stress resistance. Ascorbate may easily distribute across whole plant, amplifying stress resistance even in those organs which were not treated with Albit.
Approximately 50% effect of Albit is achieved as a result of seed treatment
(Figs. 2-4). For example, yield increase of winter wheat — 0.25 t/hà according to average
data of a lot of conducted field trials. The rest effect may be reached
with subsequent foliar spraying (yield increase of winter wheat — 0.25
t/hà).
For many years, seed treatment of winter wheat with Albit in industrial
scale has been conducted by famous seed processing
enterprises (such
as Luch (Stavropol krai, Russia) or OSEVA, Druzina, Limagrain in the
EU).

Fig. 2. Growth of seeds of winter wheat treated with Albit (40 mL/t)
in comparison with control (Scientific Institute of Biological Protection
of Plants, Krasnodar krai, 2017)

Fig. 3. Growth of seeds of barley treated with Albit in comparison with
control (Scientific Institute of Leguminous and Cereal Crops, Oryol
oblast, 2006)

Fig. 4. Influence of seed treatment with Albit on growth of barley (Scientific Institute of Leguminous and Cereal Crops, Oryol oblast, 2006)
Seed treatment of winter wheat with Albit improves field germination of
seeds (by 5-7%), protects plants against root rots and
early-leaf diseases (like Septoria leaf spot), helps form a powerful
root system (Fig. 5) (thanks to it, plants may successfully
pass winter, can resist to drought and variation of temperature) and
well-developed flag-leaf, helps increase yield by 4-15%
depending on variety, and gluten content by 1,6 abs.
% on average (2,3% to control).


Fig. 5. Development of root system of winter wheat (top)
and winter rape (bottom) (Kustodija, Lithuania,
2011)
Also, plants grown from seeds treated with Albit will pass the growth
stages by 3-12 days faster than the control plants, and form yield earlier
as a result (Fig. 6).


Fig. 6. Growth of barley (Scientific
Institute of Leguminous and Cereal Crops, Oryol oblast, 2005 –
top photo and 2006 – bottom photo). Seeds of barley were treated
with fungicide based on tiabendazol and flutriafol (1) and tank mix
with fungicide + Albit (2)
In 2006-2009, in farm Zemlyanskoe of Voronezh oblast, winter wheat (var. Don-93 and Bezenchukskaya-380)
was treated with Albit + fungicide based on tebuconazole. After Albit
treatment, number of overwintered plants of winter
wheat var. Don-93 increased from 287 plant/m2 to
319 plant/m2
(overwintering increased by 11.1% compared to the variant with pure fungicide);
number of overwintered plants of winter wheat var. Bezenchukskaya-380 –
from 309 plants/m2 to 345 plants/m2 (overwintering
increased by 11.7%). According to data of the Lithuanian Institute of
Agriculture, during snowless and frosty winter in 2013-2014, overwintering
of winter wheat after seed treatment with fungicide based on fludioxonil
was 91.6% to control, however after seed treatment with fungicide + Albit,
overwintering was 109.4% to control (overall increase by 19.4%). Field
germination of seeds increased from 93.7% to 98.1%, biological efficacy
against root rots also increased from 54.2% to 74.3%.
Seed treatment with Albit decreases the abundance of pathogenic
fungi belonging to genus Fusarium in plant rootarea
by 70-75% (according to data of Lomonosov Moscow State University).
On winter crops, Albit is also applied as antidote –
additive to pesticides for decrease of their phytotoxic effect (Fig. 7). Albit in
mixes with chemical fungicides smoothes their retardant effect, increasing
field germination. Plants grown from seeds treated with Albit are more
resistant to phytotoxic effect of herbicides. On average, based on data
of all conducted field trials (since 1997), in variants where seeds were
treated with Albit before herbicide sprays, yield was by 22.1% higher
than in variants without Albit treatment (only herbicide sprays).

Fig. 7. Influence of seed treatment with Albit on parameters
of yield and development of root rots of winter wheat (Scientific Institute
of Plant Protection, Russian Ministry of Agriculture, Voronezh oblast,
2005)
Recommended seed treatment of winter wheat and barley with Albit – 40
mL/t, rape – 60 mL/t. Adding of Albit to standard pesticides in such
small doses almost does not increase the cost of seed treatment, however
notably boosts the efficacy of pesticide treatments.
The special feature of Albit is its protective
effect of seed treatment against leaf and cauline diseases.
For example, in field trials of All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection
and All-Russia Institute of Biological Plant Protection (Krasnodar
kraj) seed treatment with Albit immunized winter wheat against soil-borne
root rot diseases during 5 months (from October of 2004 year to March
of 2005 year). Seed treatment of spring wheat and barley with Albit
decreased brown rust and Septoria leaf spot in plants by 30-42% (Kursk
Plant Protection Station, 2002). After seed treatment of sugar beet
with Albit, BE of Albit against powdery mildew in the second decade
of August was 59-66% (All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection, 2008).
In field trials of Scientific Institute of Plant Protection it was demonstrated
that application of Albit 100 mL/t on cereal crops has the same positive
effect on plants as the dosage 40 mL/t, however prolonged immunization
against foliar diseases (Septoria leaf spot, brown rust, powdery
mildew) is added up to the heading stage (Fig. 8). This dose is recommended on
a number of cereal crops.

Fig. 8. Prolonged immunization of wheat against a number
of diseases as a result of seed treatment with Albit (Scientific Institute
of Plant Protection, Russian Ministry of Agriculture, Voronezh oblast,
2007)
A high efficacy of seed treatment with
Albit on maize was proven in laboratory and field trials (see Figs. 9, 10).

Fig. 9. Positive influence of seed treatment with Albit on maize (vegetation
trial of Institute of Biochemistry and Physiology of Microorganisms,
Moscow oblast, 2005). Left photo – treatment with fungicide, right photo
– fungicide + Albit

Fig. 10. Efficacy of seed treatment with Albit on maize (field trail
was conducted in Georgia, USA, 2015). Check – control, Treated – treatment with Albit
Positive influence of seed treatment with Albit on soybean and white lupine: (Figs. 11-14).

Fig. 11. Influence of seed treatment with Albit and protectant
fungicide on growth and development of soybean plants (vegetation trial of
Institute of Biochemistry and Physiology of Microorganisms, Moscow oblast,
2007). Variants: 1 – control (without treatment), 2 – Albit, 3 – fungicide,
4 – Albit + fungicide. Albit neutralizes stress retardant effect of
protectant fungicide on soybean plants

Fig. 12. Influence of Albit on field germination, growth and
development of soybean plants (field trail was conducted in Georgia, USA, 2013).
Ñheck – control (without Albit), Treated – treatment with Albit

Fig. 13. Influence of seed treatment with various doses
of Albit on yield of soybean var. Villana (All-Russia Institute of
Biological Plant Protection, Krasnodar krai, 2009)
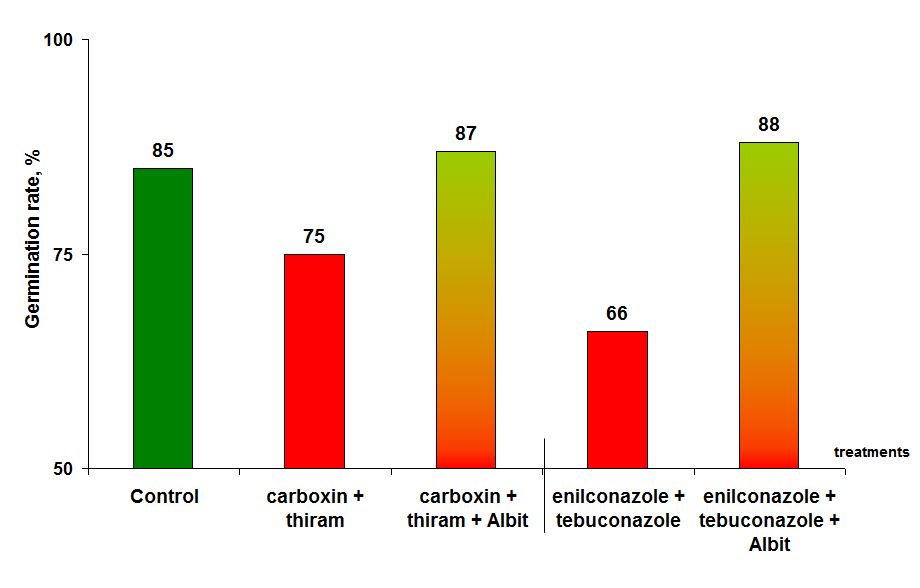
Fig. 14. The impact of Albit and different seed treatments on the field germination
rate of white lupine crops (All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of lupine Studies,
Bryansk Oblast 2019)
Currently, massive application of pesticides is widely used in agricultural
practice. However, besides their main functions (protection plants against
diseases, weeds and pests), pesticides can cause stress of plants which
they were devoted to defend. For example, at low temperature fungicides
usually have retardant effect on germs; herbicide stress, on the contrary,
is usually observed during drought. Stress effect is revealed in retarding
of growth, decreasing of seed germination, appearance of spots, burns,
leave twisting, reducing of resistance to diseases and others, resulting
in notable decrease of yield. Chemical pesticides loosing side stress
effect due to addition to Albit, reinforces their main effect. Applying
of Albit with pesticides promotes their reproducible high performance.
Head of one of the leading large-scale potato farms once said, that only
together with Albit all fungicides he used before, started working with
their full capacity, i.e., to providing 100% of the effect declared by
producer. The urgent task of modern and intensive agriculture is annual
maintenance of high yield. Especially this relates to using of generics,
which (unlike well-known plant protection products of leading producers),
as a rule, do not contain antidotes and other necessary technical means, "securing" the
effect of active ingredient (a.i.). No doubt, Albit is not a replacement
for chemical pesticides. However, application of Albit with chemical
pesticides ensures their stable and high effect even at unfavorable conditions
of vegetation season.
|